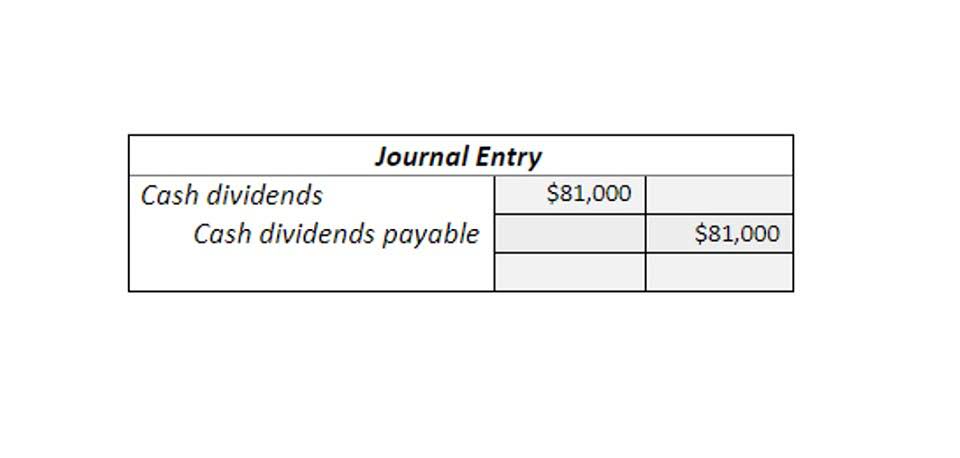
One way to assess how successful a company is in using retained money is to look at a key factor called retained earnings to market value. It is calculated over a period of time (usually a couple of years) and assesses the change in stock price against the net earnings retained by the company. Nonetheless, the accounting is similar to other deductions from the retained earnings balance. Once the transactions occur, companies will transfer the closing retained earnings balance to the upcoming year. As you can see, owner or shareholder equity is what is left over when the value of a company’s total liabilities are subtracted from the value of its assets. Once a proposed cash dividend is approved and declared by the board of directors, a corporation can distribute dividends to its shareholders.

Retained Earnings vs. Net Income: What is the Difference?
- A unique type of Expense account, Depreciation Expense, is used when purchasing Fixed Assets.
- They do not represent assets or cash balances that companies have kept.
- Each accounting period, the revenue and expenses reported on the income statement are “closed out” to retained earnings.
- Capital is essentially the residual interest in the assets of a business after deducting all of its liabilities.
- Like revenue accounts, expense accounts are temporary accounts that collect data for one accounting period and are reset to zero at the beginning of the next accounting period.
In some industries, revenue is called gross sales because the gross figure is calculated before any deductions. The decision to retain earnings or to distribute them among shareholders is usually left to the company management. However, it can be challenged by the shareholders through a majority vote because they are the real owners of the company. Retained earnings are also called earnings surplus and represent reserve money, which is available to company management for reinvesting back into the business. When expressed as a percentage of total earnings, it is also called the retention ratio and is equal to (1 – the dividend payout ratio).
► Income or Revenue
Another unique account is Accumulated Depreciation—a contra-account. Accumulated Depreciation is used to offset the Asset account for the item. Depreciation can be very complicated, so I recommend seeing your Accountant for help Interior Design Bookkeeping with the depreciation of Assets. Assets can be defined as objects or entities, both tangible and intangible, that the company owns that have economic value to the business.
11 Dividends

We’ll now move to a modeling exercise, Online Accounting which you can access by filling out the form below. Balance sheet は、略してB/S 、ほか Statement of financial position とも呼ばれます。 ⑧ Other income には、Interest income(受取利息)や Dividends income(受取配当金)などが含まれます。 ④ Gross profit から ⑤ Distribution costs(販売費)と ⑥ Administrative expense(管理費)を合わせた Operating expense(営業費用)を引いて、⑦ Operating profit(営業利益)を表示します。 損益計算書は、略してI/S や P/L 、ほか Profit and loss または Profit and loss account、Statement of operations とも呼ばれます。 Explore Social Capital’s venture capital investment strategy and portfolio exits in this insightful article.
What is Economic Profit? Understanding True Business Performance Beyond Accounting Numbers
- ① Current assets(流動資産)、② Non-current assets(固定資産)、③ Current liabilities(流動負債)、④ Non-current liabilities(固定負債) を記入し、⑤ Equity(資本) の欄には 保有する資産の残高を記入します。
- Assets are what a company owns, such as cash, inventory, and property.
- A financial statement is a formal document that shows financial health, business performance, and many more.
- Liabilities are classified as current liabilities or long-term liabilities.
- If a company’s retained earnings are less than zero, it is referred to as an accumulated deficit.
Paying off high-interest debt also may be preferred by both management and shareholders, instead of dividend payments. Alternatively, companies take the net income for the period to the retained earnings account first. Subsequently, they subtract any declared dividends from that balance. Compare total liabilities and equity with total assets and other financial ratios (like debt-to-equity) to assess financial health and risk levels. Liabilities are the debts, or financial obligations of a business – the money the business owes to others. Liabilities are classified as current liabilities or long-term liabilities.

On top of that, retained earnings are ultimately the right of a company’s shareholders. Other transactions may also decrease the retained earnings balance. Usually, these include special dividends that differ from the year-end allotments. There are times when company owners must invest their own money into the company. Equity may be in assets such as buildings and equipment, or cash. Long-term liabilities, or non-current liabilities, are typically mortgages or loans is retained earnings a current liability used to purchase or maintain fixed assets, and are paid off in years instead of months.
The “Retained Earnings” line item is recognized within the shareholders’ equity section of the balance sheet. In simple words, the retained earnings metric reflects the cumulative net income of the company post-adjustments for the distribution of any dividends to shareholders. The retained earnings of a company are the total profits generated since inception, net of any dividend issuances to shareholders. Retained earnings on a balance sheet are essentially the profits that a company has made over time, but hasn’t distributed to its owners as dividends. A company’s capital stock, also known as shareholders’ equity, is the amount of money invested by its owners.